5.8 KiB
BITE - A Basic/IoT/Example
Playing with IoT
This project is for educational purposes only. It does not implement any authentication and/or encryption protocol, so it is not suitable for real production.
Future implementations
- Broker HA via VerneMQ clustering
- Stream analytics via Apache Spark
Installation
Requirements
moby-engineorpodman-docker(recommended)docker-compose
The project is compatible with Docker for Windows (using Linux executors), but it is advised to directly use a minimal Linux VM instead (via the preferred hypervisor).
Podman
podman, with podman-docker is the recommended way to run BITE, in rootless mode.
systemctl start --user podman.socket
export DOCKER_HOST=unix://run/user/$UID/podman/podman.sock
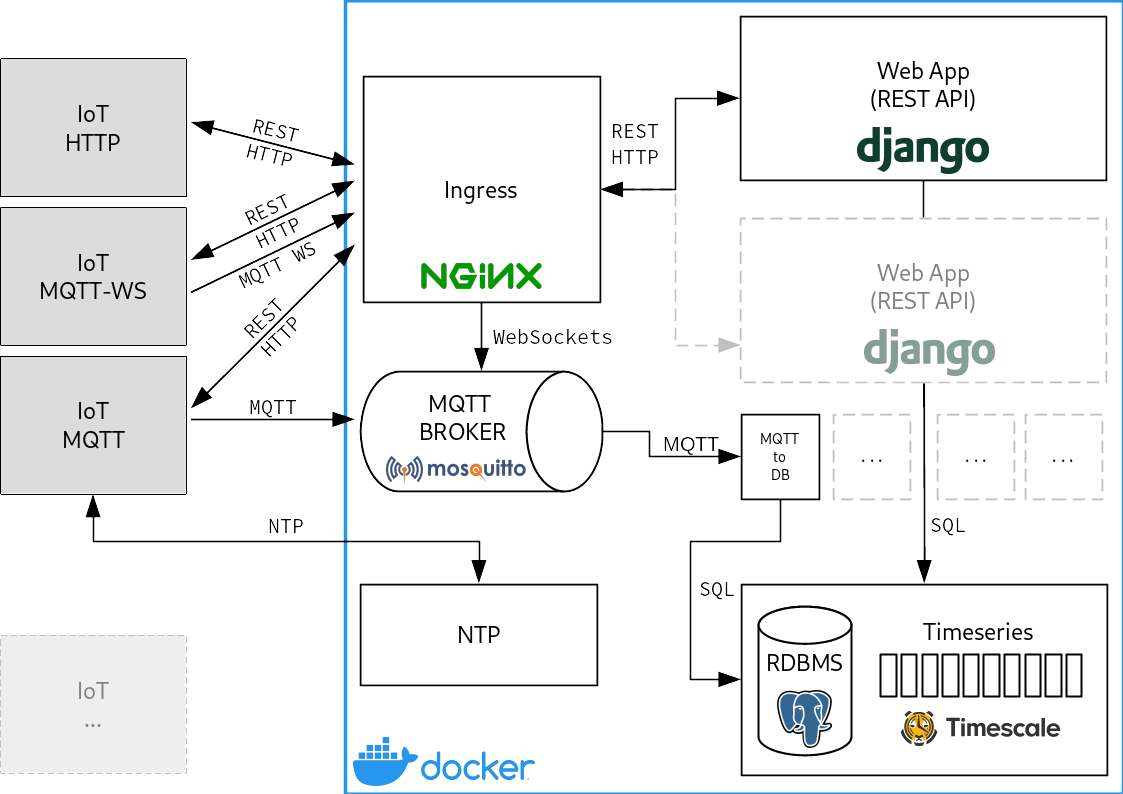
Application stack
The application stack is composed by the following components:
- Django with
Django REST framework
web application (running via
gunicornin production mode)mqtt-to-dbcustom daemon to dump telemetry into the timeseries database- telemetry payload is stored as json object (via PostgreSQL JSON data type)
- Timescale DB, a PostgreSQL database with a timeseries extension
- Mosquitto MQTT broker (see alternatives below)
- Nginx as ingress for HTTP (see alternative below)
- Chrony as NTP server
(with optional
MD5encryption)
Deployment
The $CUSTOM_DOCKER_IP environment variable can be used to set a custom
IP address to bind ports. Default is 0.0.0.0; 127.0.0.1 is a
safe configuration (see https://github.com/docker/compose/issues/2999).
Development, using image code
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml build
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -d [--scale {bite,mqtt-to-db)=N]
It exposes:
http://localhost:80(HTTP and MQTT over Websockets)tcp://localhost:1883(MQTT)udp://localhost:123(NTP)
Django runs with DEBUG = True and SKIP_WHITELIST = True
Development with direct access to services and autoreload
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.dev.yml up -d [--scale {bite,mqtt-to-db)=N]
It exposes:
http://localhost:80(HTTP and MQTT over Websockets)http://localhost:8080(Django'srunserver)tcp://localhost:1883(MQTT)tcp://localhost:9001(MQTT over Websockets)udp://localhost:123(NTP)tcp://localhost:5432(PostgreSQL/Timescale)
Django runs with DEBUG = True and SKIP_WHITELIST = True
Production (kind of...)
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.prod.yml up -d [--scale {bite,mqtt-to-db)=N]
It exposes:
http://localhost:80(HTTP and MQTT over Websockets)tcp://localhost:1883(MQTT)udp://localhost:123(NTP)
Django runs with DEBUG = False and SKIP_WHITELIST = False
Extra features
The project provides multiple modules that can be combined with the fore-mentioned configurations.
Traefik
To use Traefik instead of Nginx use:
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -f docker/ingress/docker-compose.traefik.yml -d
VerneMQ
A ~8x memory usage can be expected compared to Mosquitto.
To use VerneMQ instead of Mosquitto run:
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -f docker/mqtt/docker-compose.vernemq.yml -d
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ does provide AMQP protocol too, but ingestion on the application side is not implemented yet. A ~10x memory usage can be expected compared to Mosquitto.
To use RabbitMQ (with the MQTT plugin enabled) instead of Mosquitto run:
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -f docker/mqtt/docker-compose.rabbitmq.yml -d
EDGE gateway simulation (via dind)
An EDGE gateway, with containers as modules, may be simulated via dind (docker-in-docker).
Start the EDGE
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -f docker/edge/docker-compose.edge.yml -d
Run the modules inside the EDGE
DOCKER_HOST='127.0.0.1:22375' docker-compose -f docker-compose.modules.yml up -d [--scale {device-http,device-ws,device-mqtt}=N]
Arduino
A simple Arduino UNO sketch is provided in the arduino/tempLightSensor folder.
The sketch reads temperature and light from sensors.
/* ... */
void loop(void) {
const int postDelay = TELEMETRY_DELAY * 1000;
unsigned int tempReading = analogRead(A0);
unsigned int photocellReading = analogRead(A1);
float tempVoltage = tempReading * AREF_VOLTAGE / 1024.0;
float tempC = (tempVoltage - 0.5) * 100 ;
if (NTPValid) {
telemetry["clock"] = timeClient.getEpochTime();
} else {
telemetry["clock"] = NULL; // converted into 0
}
payload["light"] = photocellReading;
temp["celsius"] = tempC;
temp["raw"] = tempReading;
temp["volts"] = tempVoltage;
#if USE_MQTT
publishData(config, telemetry);
#else
postData(config, telemetryURL, telemetry);
#endif
/* ... */
Testing
Application tests are part of the Django suite:
python manage.py test
End-to-End tests are performed via Travis-CI. See .travis.yml
for further explanations.